⚛️Revertron on Nostr: About social contagions: In 1972, British psychologist Gerald Russell treated a woman ...
About social contagions:
In 1972, British psychologist Gerald Russell treated a woman with an unusual eating disorder involving binging and purging. Over the next 7 years, he saw a further 30 woman presenting with the same condition.
In 1979, he wrote a paper published in Psychological Medicine, in which he gave it the name bulimia nervosa. The condition was included in the DSM-III the following year. Then something remarkable happened. The illness swept the globe like wildfire affecting an estimated 30 million people by the mid-1990s, the majority of whom were teenage girls and young women.
The explanation for this rapid spread is what philosopher Ian Hacking calls 'semantic contagion' - how the process of naming and describing a condition creates the means by which the condition spreads. The epidemic of multiple-personality disorder in the 90s was spread this way Bulimia entered the lexicon via women's magazines such as Mademoiselle and Better Homes and Gardens, which ran stories about this new and worrying disorder affecting women and girls. Multiple studies demonstrate the media's culpability in the spread of social contagions.
In the first decade of the 21st century, the seeds were sown for another global contagion. A rights movement that started out with the aim of improving the lives of transgender people has given rise to a new type of gender dysphoria with all the hallmarks of a social contagion.
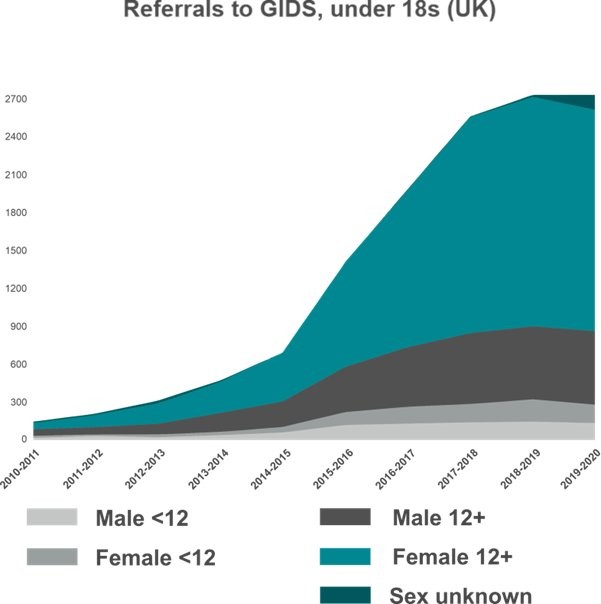
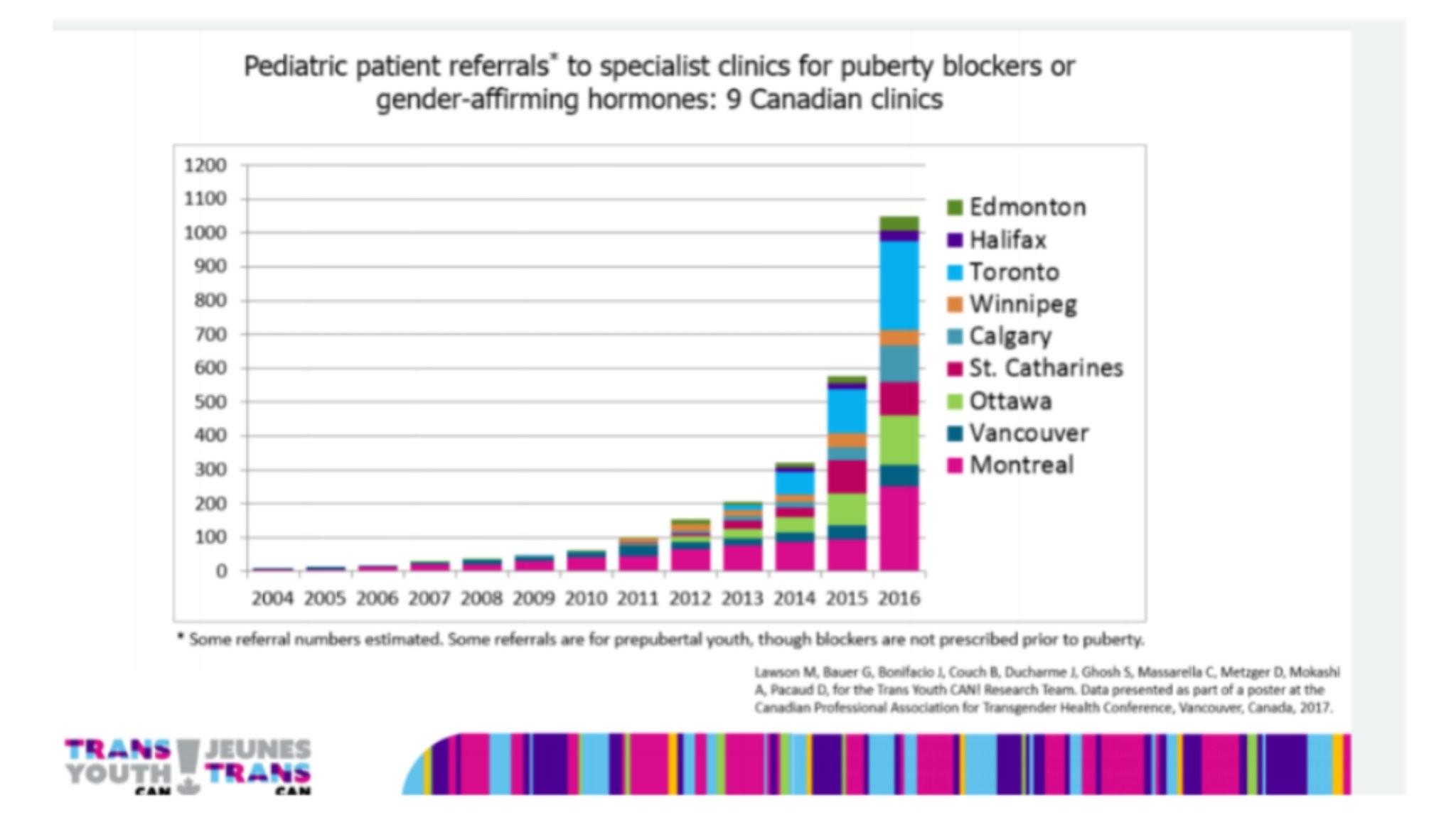
Just like bulimia, gender dysphoria was virtually unheard of in the teenage girl population prior to 2010, and then, all of a sudden, countries all over the industrialised world saw an explosion of adolescent girls identifying as transgender.
It was the perfect storm. In the 2010s, the media fascination with transgenderism began with 'Caitlyn' Jenner and I Am Jazz; the political left became infatuated with trans rights, and schools started teaching gender ideology to children as young as kindergarten.
Social media came on the scene and provided the perfect super-spreading environment. Teenage girls are now just one click away from 1000s of TikTok and YouTube videos of young women proudly showing off their mastectomy scars and extolling the joy of taking testosterone.
Just as this new, atypical type of gender dysphoria was emerging, gender clinics, at the behest of activist groups, abandoned the psychotherapeutic approach of watchful waiting and adopted the affirmative model - fast-tracking these teens to irreversible medical procedures.
We're in the eye of the storm right now, so most people can't see the damage being done. But soon, all the young people emerging from this contagion sterile and missing body parts will be visible for all to see, and people will be horrified that they supported such evil.
#trans #transgender #transgenderism #science #psychology #gender #genderDysphoria
In 1972, British psychologist Gerald Russell treated a woman with an unusual eating disorder involving binging and purging. Over the next 7 years, he saw a further 30 woman presenting with the same condition.
In 1979, he wrote a paper published in Psychological Medicine, in which he gave it the name bulimia nervosa. The condition was included in the DSM-III the following year. Then something remarkable happened. The illness swept the globe like wildfire affecting an estimated 30 million people by the mid-1990s, the majority of whom were teenage girls and young women.
The explanation for this rapid spread is what philosopher Ian Hacking calls 'semantic contagion' - how the process of naming and describing a condition creates the means by which the condition spreads. The epidemic of multiple-personality disorder in the 90s was spread this way Bulimia entered the lexicon via women's magazines such as Mademoiselle and Better Homes and Gardens, which ran stories about this new and worrying disorder affecting women and girls. Multiple studies demonstrate the media's culpability in the spread of social contagions.
In the first decade of the 21st century, the seeds were sown for another global contagion. A rights movement that started out with the aim of improving the lives of transgender people has given rise to a new type of gender dysphoria with all the hallmarks of a social contagion.
Just like bulimia, gender dysphoria was virtually unheard of in the teenage girl population prior to 2010, and then, all of a sudden, countries all over the industrialised world saw an explosion of adolescent girls identifying as transgender.
It was the perfect storm. In the 2010s, the media fascination with transgenderism began with 'Caitlyn' Jenner and I Am Jazz; the political left became infatuated with trans rights, and schools started teaching gender ideology to children as young as kindergarten.
Social media came on the scene and provided the perfect super-spreading environment. Teenage girls are now just one click away from 1000s of TikTok and YouTube videos of young women proudly showing off their mastectomy scars and extolling the joy of taking testosterone.
Just as this new, atypical type of gender dysphoria was emerging, gender clinics, at the behest of activist groups, abandoned the psychotherapeutic approach of watchful waiting and adopted the affirmative model - fast-tracking these teens to irreversible medical procedures.
We're in the eye of the storm right now, so most people can't see the damage being done. But soon, all the young people emerging from this contagion sterile and missing body parts will be visible for all to see, and people will be horrified that they supported such evil.
#trans #transgender #transgenderism #science #psychology #gender #genderDysphoria

