Event JSON
{
"id": "82ea81edb66147067ecbc1de94bc989ae50eee6ee410a398e504097d348fec5d",
"pubkey": "b86894af7f544cdad086d4ec01384e91512f484914e6141795547f21268740dd",
"created_at": 1734330624,
"kind": 1,
"tags": [
[
"t",
"wind"
],
[
"t",
"sea"
],
[
"t",
"warming"
],
[
"t",
"acidification"
],
[
"imeta",
"url https://s3.eu-central-2.wasabisys.com/mastodonworld/media_attachments/files/113/661/090/755/788/855/original/a1d31957793947aa.png",
"m image/png",
"dim 2000x1820",
"blurhash UgO|CORlkBoy00V@fkoeD$t7jZWVM{ocofju"
],
[
"proxy",
"https://mastodon.world/users/ombialik/statuses/113661091809456900",
"activitypub"
]
],
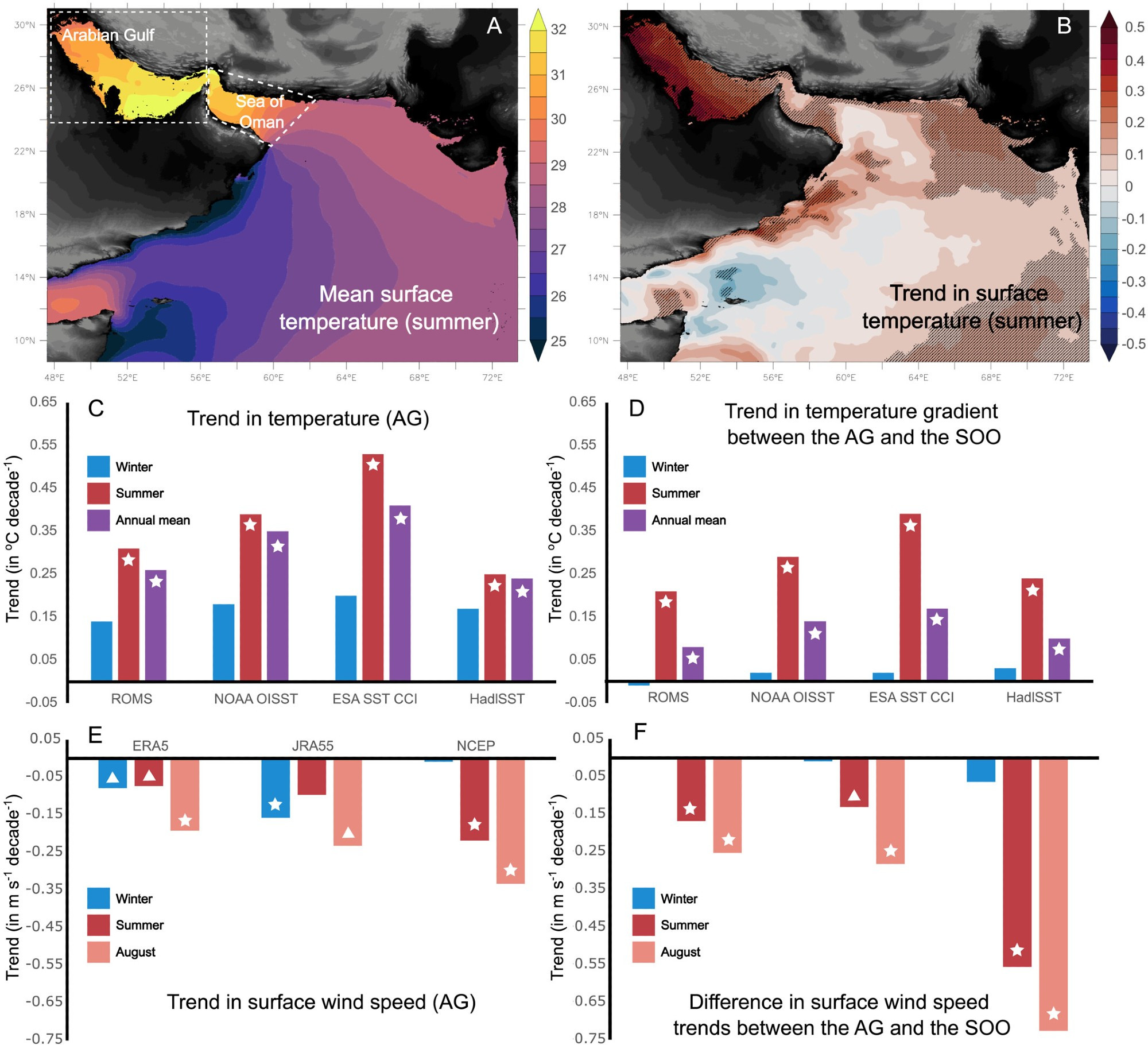
"content": "Shifting #wind patterns have a lot of knock-on effects. In shallow seas (like ancient epicontinental #sea), those can be rather dramatic. Take the Persian/Arabian Gulf; a great modern case study. There, weakening winds have contributed to rapid #warming, deoxygenation, and #acidification. \nhttps://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2024GL109898\n\nhttps://s3.eu-central-2.wasabisys.com/mastodonworld/media_attachments/files/113/661/090/755/788/855/original/a1d31957793947aa.png",
"sig": "a1e9893d90cca5046a1e9c971a502a9be471bc9d442d7b9d3b98ad67983fcb2c6a6b24fe22fff150519d8cca3f9c97ebf52454e300ad90397fce62e2223bf3a4"
}